Why Cross-Cultural Competence Isn't Optional Anymore

In our interconnected world, interacting with people from diverse cultural backgrounds is now the norm. This shift has significant implications for both businesses and individuals. Organizations increasingly rely on global teams, international partnerships, and diverse customer bases. This demands a workforce skilled in navigating cultural nuances.
Building cross-cultural competence is crucial for success in today's professional world. This goes beyond simply knowing the "dos and don'ts" of different cultures. It involves developing a genuine appreciation for diverse perspectives and communication styles.
It means moving beyond surface-level awareness to cultivate empathy and adaptability. Understanding the difference between fitting in and truly adding value to a culture is key. For more on this important distinction, see this article about the importance of Culture Fit vs Culture Add.
The Rising Demand for Cross-Cultural Skills
The growing importance of cross-cultural competence is evident in the expanding cross-cultural training market. This market reached $1.32 billion in 2024. It's projected to reach $1.81 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.8%.
This growth is fueled by factors such as the rise of international travel, remote work, and corporate social responsibility initiatives. You can find more detailed statistics here. This surge highlights the increasing recognition of cultural intelligence as a core competency.
The Consequences of Cultural Incompetence
Conversely, a lack of cross-cultural competence can create significant challenges. Misunderstandings, miscommunication, and even conflicts can arise when individuals fail to appreciate cultural differences. This can damage relationships and hinder productivity, impacting an organization's bottom line.
Missed opportunities, failed negotiations, and damaged reputations can also be costly consequences of cultural insensitivity. This further emphasizes the need to invest in cross-cultural competence development.
In conclusion, developing cross-cultural competence is no longer a luxury but a necessity. It's a key driver of success for individuals and organizations aiming to thrive in the increasingly diverse global marketplace. By embracing cultural intelligence, we unlock new opportunities, build stronger relationships, and create a more inclusive world.
The Five Core Pillars of Cultural Intelligence
Developing cross-cultural competence isn't about memorizing facts. It's about cultivating a mindset and skillset that empowers you to navigate intercultural interactions with grace and effectiveness. This journey involves strengthening five core pillars of cultural intelligence.
These pillars provide a framework for understanding and interacting with people from all walks of life. They offer a pathway to building bridges and fostering genuine connection in our increasingly diverse world.
Cultural Self-Awareness
This pillar is the foundation. It's about understanding your own cultural programming – the values, beliefs, and biases you've internalized. Recognize how your background influences your perceptions and judgments of others. This self-awareness is the first step toward truly understanding and appreciating others. Developing this often involves improving your understanding of emotional intelligence.
Understanding yourself is crucial to understanding others. By recognizing your own cultural lens, you can begin to see the world through the eyes of others.
Knowledge Acquisition
Knowledge Acquisition means going beyond stereotypes. Develop systematic approaches to learning about other cultures. It’s not about accumulating facts, but understanding the values and assumptions that drive behaviors. This opens the door to empathy and genuine connection.
Seek to understand the "why" behind cultural differences. This deeper understanding fosters respect and allows you to build stronger relationships.
Mindset Cultivation
Cultivating the right mindset is essential for cross-cultural competence. Develop genuine curiosity, empathy, and the ability to suspend judgment. Even when confronted with the unfamiliar, an open mind allows for deeper learning and more meaningful connections.
Embrace the unknown with a spirit of curiosity and a willingness to learn. This open-mindedness is key to unlocking the richness of cultural diversity.
Adaptability Skills
Adaptability is the ability to modify your behavior appropriately in different cultural contexts. This isn’t about losing your authenticity. It’s about learning to communicate and interact in ways that are respectful and effective. It's about finding common ground while celebrating differences.
Adapt your communication style to build rapport and understanding. This flexibility will help you navigate intercultural interactions with ease.
Experience Integration
This final pillar focuses on continuous growth. Reflect on your experiences, identify your strengths and weaknesses, and continually refine your approach. Transform everyday interactions into opportunities for growth and deeper understanding.
Each interaction is a chance to learn and grow. Embrace these opportunities to refine your approach and deepen your cross-cultural competence.
To illustrate these five pillars further, let's take a look at the following table:
This table provides a detailed breakdown of the Five Pillars of Cross-Cultural Competence, outlining the core concepts, key development activities, and common challenges associated with each pillar.
| Pillar | Core Concept | Key Development Activities | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Self-Awareness | Understanding your own cultural programming and biases | Reflecting on your own values, beliefs, and behaviors; seeking feedback from others; exploring your cultural heritage | Difficulty recognizing personal biases; defensiveness when confronted with cultural differences |
| Knowledge Acquisition | Moving beyond stereotypes and developing systematic approaches to learning about other cultures | Conducting research; engaging with diverse communities; participating in cultural exchange programs | Relying on stereotypes; overgeneralizing cultural information |
| Mindset Cultivation | Developing genuine curiosity, empathy, and the ability to suspend judgment | Practicing mindfulness; engaging in perspective-taking exercises; challenging your own assumptions | Resistance to change; difficulty accepting ambiguity |
| Adaptability Skills | Modifying your behavior appropriately in different cultural contexts | Practicing active listening; adapting your communication style; developing flexibility and resilience | Fear of making mistakes; discomfort with unfamiliar customs |
| Experience Integration | Learning from your cross-cultural encounters and continually refining your approach | Reflecting on past experiences; seeking feedback; integrating new learning into future interactions | Difficulty applying learning to new situations; lack of reflection |
By actively engaging with each pillar, you can embark on a journey of personal and professional growth, fostering more effective and harmonious intercultural relationships.
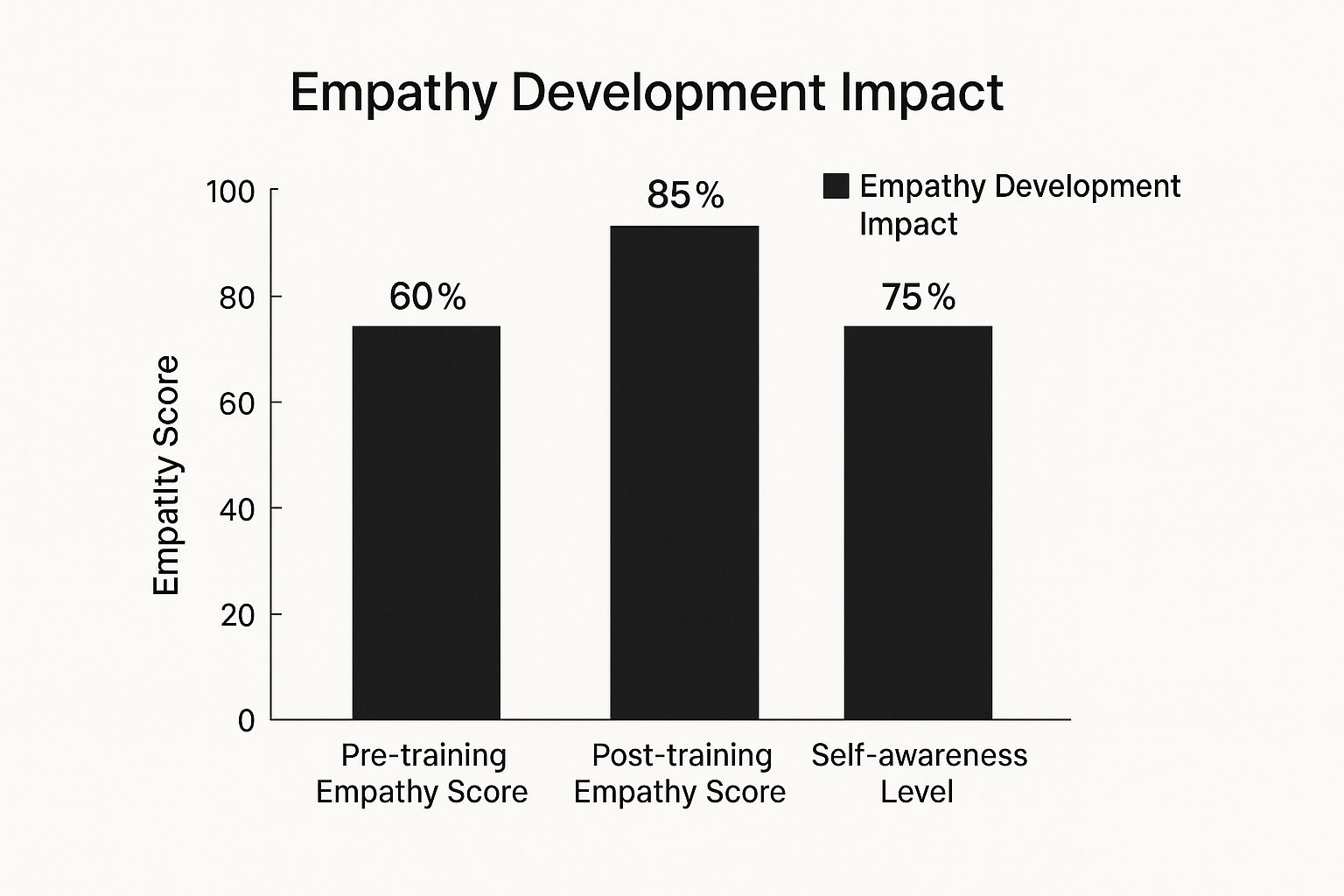
The infographic above visually represents the impact of empathy development on cross-cultural competence. It shows pre- and post-training empathy scores, along with self-awareness levels. Focused training can significantly boost empathy (from 60% to 85%), highlighting its vital role in cross-cultural competence. A strong self-awareness score of 75% further emphasizes the connection between understanding yourself and understanding others. Through dedicated efforts in developing these five pillars, individuals and organizations can unlock incredible potential, fostering a more interconnected and understanding global community.
The Business Case: When Cultural Intelligence Drives Profit

Developing cross-cultural competence offers benefits that reach far beyond simply fostering goodwill. Cultural intelligence has a direct and measurable impact on tangible business advantages, influencing profitability and global reach. In essence, it's about understanding the profound impact cultural sensitivity can have on your bottom line. This section explores why prioritizing cross-cultural competence is not only ethically responsible but also financially rewarding.
Real-World Success Stories
Companies that actively invest in cross-cultural training programs are seeing remarkable returns. Cisco, for example, has saved millions by significantly reducing its expatriate failure rate through targeted cultural training. This clearly demonstrates how investing in employees' cultural understanding can minimize costly turnover and boost overall project success rates.
HSBC also recognized a direct link between its cultural competence initiatives and a measurable increase in market share within emerging economies. Understanding local cultures can unlock access to new markets and fuel business growth. These real-world examples underscore the significant impact of cultural intelligence on achieving lasting business success.
The Cost of Cultural Insensitivity
Overlooking the importance of cross-cultural competence can have detrimental effects, leading to expensive mistakes and lost opportunities. One company's product launch in Asia was severely hampered by a $700 million translation error. This highlights the critical need for meticulous attention to detail regarding language and cultural nuances in international business.
Even seemingly small cultural missteps can damage international partnerships before they even have a chance to flourish. These oversights can erode trust and ultimately contribute to failed ventures. Cross-cultural competence is not a luxury; it's a necessity for businesses operating on a global scale, directly impacting their ability to thrive in diverse markets.
A significant challenge for global businesses is expatriate failure, which can be a considerable expense. However, the global cross-cultural training market is predicted to reach USD 1928.2 million by 2029, with a projected CAGR of 6.8%. This growth reflects the growing recognition of the importance of cross-cultural training in achieving international business success. Explore this topic further.
Innovation and Cross-Cultural Teams
Well-managed, cross-cultural teams consistently outperform homogeneous teams when it comes to innovation. The diverse perspectives inherent in these teams foster creativity and enhance problem-solving abilities, ultimately leading to more innovative solutions. Diversity, when combined with effective cross-cultural management, becomes a powerful engine for innovation. Simply assembling a diverse team isn’t enough; actively managing cultural dynamics is essential for maximizing team performance.
Measuring the ROI of Cultural Competence
Developing cross-cultural competence offers a measurable return on investment. By carefully calculating the cost of cultural misunderstandings and weighing them against the benefits of successful cross-cultural interactions, organizations can quantify the true value of these initiatives. Frameworks exist for calculating the ROI of cultural competence programs, helping organizations clearly demonstrate the financial impact of these vital investments. This data-driven approach allows businesses to make informed decisions about investing in cultural intelligence training and initiatives.
Next-Gen Approaches to Building Cultural Intelligence
Traditional cultural sensitivity workshops often fall short. They simply don't prepare individuals for the real-world complexities of cross-cultural interactions. This means organizations must adapt. They must embrace more effective and engaging methods for developing cross-cultural competence. This section explores exciting new approaches that are changing how we build cultural intelligence.
Immersive Learning Through VR
Imagine stepping into a virtual boardroom in Tokyo. You're negotiating a major deal, all before ever boarding a plane. This is the power of Virtual Reality (VR) training. VR programs offer realistic simulations of cross-cultural scenarios. This gives individuals a safe, controlled environment to practice their skills.
For example, executives can use simulated environments to navigate high-stakes international negotiations. This builds their confidence and competence before facing similar real-world situations. It's a powerful way to prepare for the challenges of global business.
AI-Powered Cultural Coaching
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also changing the game. AI-powered cultural coaches provide personalized, real-time guidance during actual cross-border interactions. Imagine having instant access to insights on cultural nuances, communication styles, and potential misunderstandings.
These tools empower individuals to navigate complex situations effectively. This personalized feedback significantly accelerates the development of cross-cultural competence, leading to stronger, more productive interactions.
Gamified Microlearning: Making Learning Stick
Forget lengthy lectures and dry textbooks. Gamified microlearning offers a fresh approach. It breaks down complex cultural concepts into bite-sized, engaging modules. This method uses game mechanics and interactive elements to make learning fun and, more importantly, effective.
Microlearning also lets individuals learn at their own pace, reinforcing concepts over time. This has been proven to drastically improve knowledge retention compared to traditional training methods. It's about making learning engaging and sustainable.
To understand the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, take a look at the comparison below:
Modern Cross-Cultural Training Methods Comparison
Analysis of emerging training methods with their advantages, disadvantages, and best applications
| Training Method | Key Benefits | Limitations | Best For | Cost Range | Effectiveness Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immersive Learning Through VR | Realistic simulations, safe practice environment, increased confidence | High implementation cost, potential for motion sickness, requires specialized equipment | High-stakes scenarios, international negotiations, complex cultural interactions | High | High |
| AI-Powered Cultural Coaching | Personalized feedback, real-time guidance, improved communication | May not fully replicate human interaction, requires internet access, data privacy concerns | On-the-job training, cross-border communication, navigating cultural nuances | Medium | Medium-High |
| Gamified Microlearning | Improved knowledge retention, engaging and fun, flexible learning pace | Requires ongoing content development, may not be suitable for all learning styles, needs reliable internet access | Reinforcing concepts, bite-sized learning, diverse cultural topics | Low-Medium | Medium |
This table highlights the variety of new methods available and helps illustrate the key differences in cost, effectiveness, and ideal applications. Choosing the right approach depends on your specific needs and resources.
This innovative market is on the rise. The cross-cultural training market is projected to grow by USD 1.93 billion between 2025 and 2029. This growth is fueled by the rise of cost-effective e-learning modules and AI-powered training tools. Discover more about this market growth.
Finding The Right Approach
While these next-generation approaches offer exciting possibilities, they also have limitations. VR training can be expensive. AI coaches, while effective, may not fully capture the nuances of human interaction.
Choosing the right method depends on several factors. These include your organizational context, budget, and learning goals. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for creating truly effective cross-cultural training initiatives.
Measuring What Matters: Beyond Self-Reported Competence

While self-assessment can be a valuable starting point, relying solely on individuals to evaluate their own cross-cultural competence can be misleading. Self-perceptions don't always accurately reflect actual skills and behaviors. This section explores practical strategies and validated assessment tools for accurately measuring cross-cultural competence. These tools offer a more objective and reliable understanding of an individual's true capabilities, leading to focused development plans and ultimately, stronger cross-cultural interactions.
Validated Assessment Tools for Cross-Cultural Competence
Several validated assessment tools provide a more objective evaluation of cross-cultural competence than self-assessment alone. Many global organizations rely on these tools for valuable insights. One widely used tool is the Intercultural Development Inventory (IDI). The IDI assesses an individual's orientation towards cultural differences, offering insights into their current stage of intercultural sensitivity.
Another valuable tool is the Cultural Intelligence Scale (CQS). The CQS measures four key aspects of cultural intelligence: cognitive, motivational, behavioral, and metacognitive. Each of these factors contributes significantly to an individual's ability to adapt and succeed in diverse cultural environments. The Global Competencies Inventory (GCI) further expands this assessment by evaluating an individual’s global mindset, including their comfort with ambiguity and skill in building international relationships.
Quantifying Cultural Competence in the Real World
Leading international companies use these assessment tools to quantify cultural competence, recognizing the direct link between cultural intelligence and real-world performance. These assessments move beyond subjective self-evaluations, providing quantifiable data that can be analyzed to predict an individual's effectiveness in navigating diverse cultural settings, managing global teams, and succeeding in international business.
Evaluating Team-Level Cultural Intelligence
Developing cross-cultural competence isn't just about individual skills; it’s also about fostering strong, effective cross-cultural teams. Measuring team-level cultural intelligence provides unique insights into the strengths and weaknesses of team interactions across cultural differences. This information allows for targeted interventions to improve communication, collaboration, and overall team performance.
Establishing Meaningful Metrics and Demonstrating ROI
To fully understand the impact of cross-cultural competence initiatives, organizations need to establish meaningful metrics. This involves tracking progress over time, measuring the effectiveness of training programs, and demonstrating a tangible return on investment (ROI). By connecting cross-cultural competence development to specific business outcomes, organizations can showcase the value of these initiatives and secure ongoing support and investment.
Selecting the Right Assessment Method
No single assessment tool fits every situation. Organizations should carefully consider their unique goals, context, and available resources when selecting a method. This strategic approach ensures the chosen tool aligns with the organization's specific needs and provides valuable, actionable insights to guide development efforts. By avoiding common measurement pitfalls and using assessment results to create targeted development plans, organizations can cultivate genuine cross-cultural capabilities – essential for success in today's increasingly interconnected global marketplace.
Your 90-Day Cross-Cultural Competence Acceleration Plan
This plan helps you translate abstract cultural concepts into practical actions. It's a personalized roadmap to develop your cross-cultural skills, built on proven methods used by diplomatic corps and multinational corporations. Over 90 days, this framework guides you through five sequential phases, building practical skills and enabling you to measure your progress.
Phase 1: Reality-Based Self-Assessment (Days 1-15)
Begin with an honest evaluation of your current cross-cultural competence. This isn't about how you perceive yourself, but a structured analysis of your skills across key areas. Use established tools like the Intercultural Development Inventory (IDI) or the Cultural Intelligence Scale (CQS) for a data-driven starting point. Identify your strengths and weaknesses in areas such as cultural self-awareness, acquiring knowledge, and adaptability.
Phase 2: Goal Setting and Contextualization (Days 16-30)
After assessing your current skills, define SMART development goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound). Connect these goals to your professional life. Are you getting ready for an international assignment? Forming a global team? Expanding into new markets? Your goals should directly support these aims. For instance, if you're leading a multicultural team, a goal could be improving your communication style to be more inclusive.
Phase 3: Resource Identification and Learning Strategy (Days 31-45)
Now, identify the right resources and learning strategies. Consider your learning style, budget, and available time. This might involve formal cross-cultural training programs offered by organizations like the Global Human Resource Institute, immersive language learning, or AI-powered cultural coaching tools. A blend of online resources and in-person workshops might be the perfect fit. Aligning your resources with how you learn best is key to absorbing knowledge effectively.
Phase 4: Structured Action Plan and Accountability (Days 46-75)
With your chosen resources, create a structured 30-day action plan. Divide your main goals into smaller, actionable steps. Schedule specific activities, like attending a webinar on cross-cultural communication or practicing active listening with colleagues from different backgrounds. Building in accountability is crucial. Find a mentor, join a study group, or regularly track your progress. Accountability keeps you focused and helps you avoid abandoning your development goals.
Phase 5: Progress Measurement and Refinement (Days 76-90)
The final phase focuses on measuring your progress and refining your approach based on the results. Don't just rely on self-assessment – use objective measures. If your goal was to improve communication, are there fewer misunderstandings in your team? Is the feedback from colleagues more positive? Use these insights to adjust your development plan, concentrating on areas needing further attention. This iterative approach ensures continuous growth and improvement of your cross-cultural competence. Remember, developing these skills is an ongoing journey. Consistent effort and thoughtful reflection will help you succeed in our increasingly interconnected world.
Ready to advance your career by developing your cross-cultural competence? Explore the certification programs and resources available at the Global Human Resource Institute and begin your journey to global success.




0 Comments